How to Build a Robust Flutter App Initialization Flow with Riverpod
15 min read
Some useful Riverpod techniques you can use to initialize async dependencies, show some loading UI, and handle errors during app startup.

Some useful Riverpod techniques you can use to initialize async dependencies, show some loading UI, and handle errors during app startup.
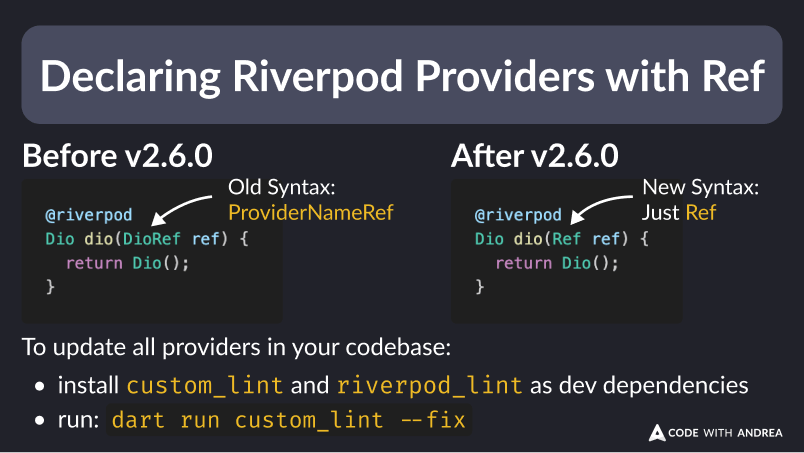
Since Riverpod 2.6.0, all generated providers can be declared with a Ref argument. Here's how to migrate to the new syntax.
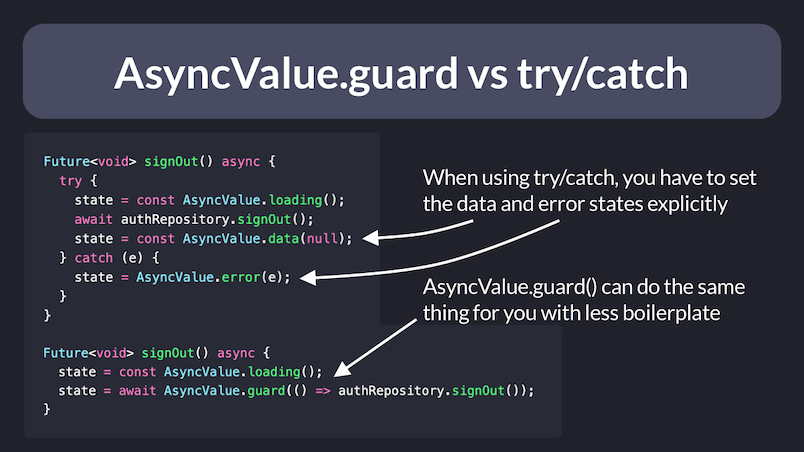
If you have many AsyncNotifier subclasses, using try/catch can be tedious. With AsyncValue.guard you get the same result with less boilerplate.
A complete guide to implementing pagination with Riverpod, covering: infinite scrolling, loading and error states, search UI, caching, and debouncing.
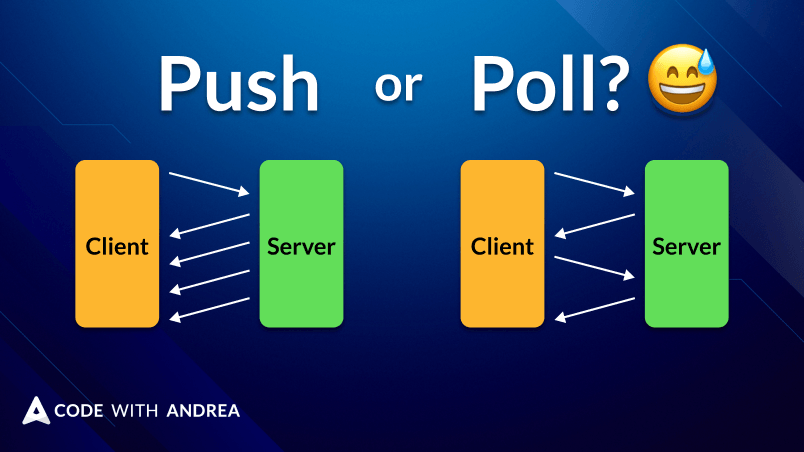
Find out when to use one-time reads and when to switch to realtime updates in Flutter development for optimal app performance and user experience.
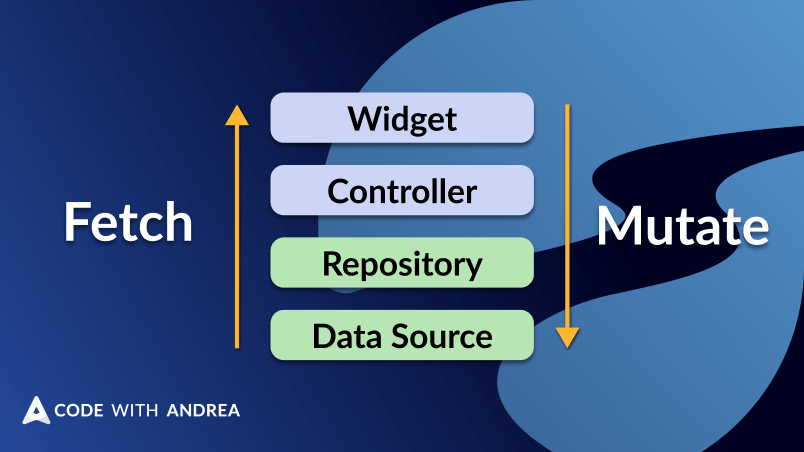
When building mobile apps, we often need to fetch and mutate data. This article explains how to do it effectively using my reference Riverpod architecture.
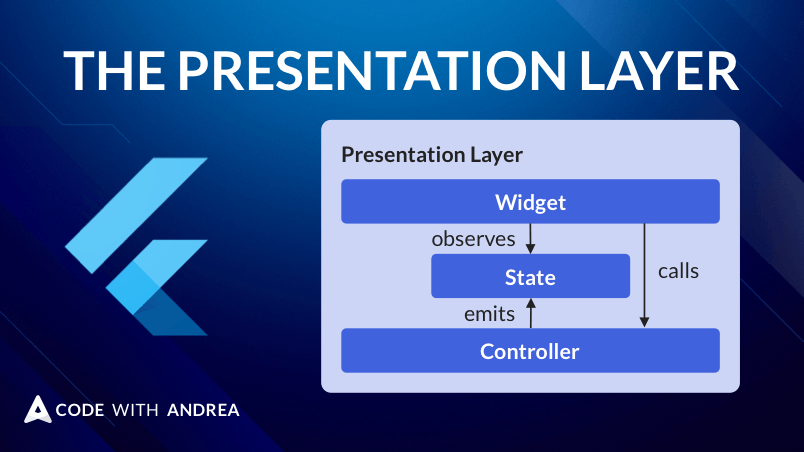
How to implement controller classes that can hold business logic, manage widget state, and interact with repositories in the data layer.
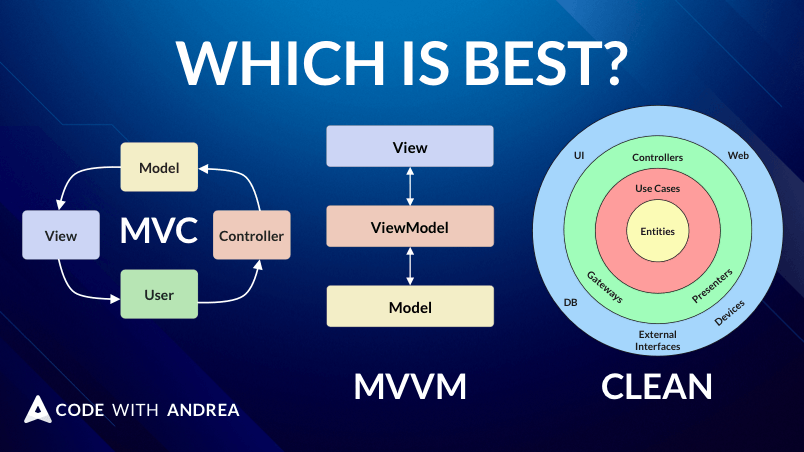
Comparing my Riverpod App Architecture with other popular ones such as MVC, MVVM, Bloc, Stacked, Clean Architecture, and Android App Architecture.
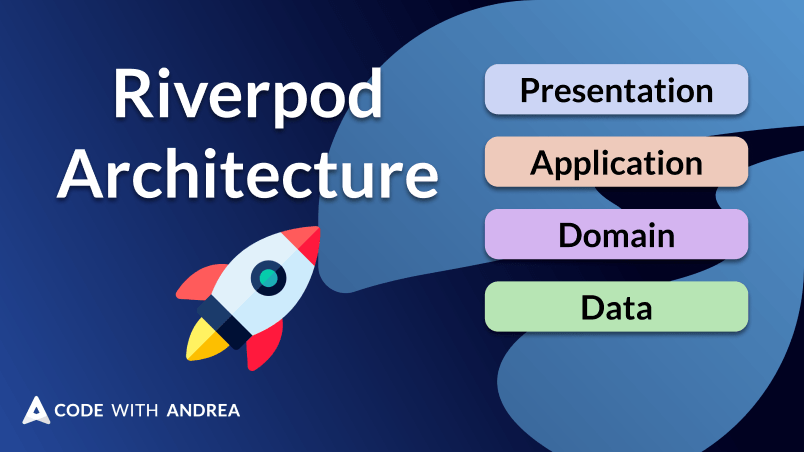
Introducing a new Riverpod App Architecture that can be used to build scalable and maintainable apps with a clear structure.
The new Riverpod Lint package adds useful lints and refactoring options that make writing Flutter apps a breeze. Here's how to make the most of it.

A step-by-step guide showing how to migrate StateProvider and StateNotifier to the new Notifier and AsyncNotifier classes (StreamNotifier is covered too).

Thanks to the new Riverpod Generator package, we no longer have to declare providers manually. This guide explains how to use the new @riverpod syntax.

AsyncNotifier does not have a mounted property and this can cause some problems in practice. This article explores some solutions and their tradeoffs.
Let's explore some techniques to separate our business logic and navigation code from the UI, using GoRouter and Riverpod.
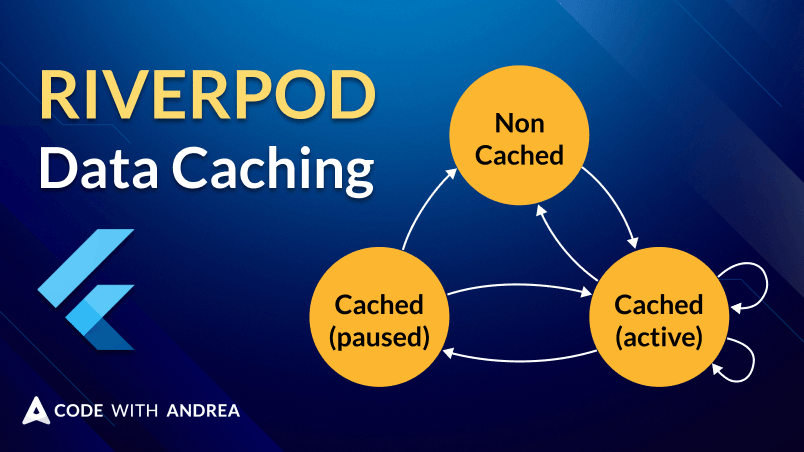
Riverpod is a powerful reactive caching and data-binding framework. Let’s learn how to make the most of it so we can use it effectively.

AsyncNotifier is great. But how do we write unit tests for it? Here are all the details and a template you can follow to test your AsyncNotifier subclasses.

A complete guide to the Riverpod package as a reactive caching and data-binding framework. Fully updated to Riverpod 2.0.
How to access localized strings outside your widgets without a BuildContext, by creating a locale-aware AppLocalizations provider using Riverpod.

An overview of how we can use Riverpod to register listeners and initialize complex objects with dependencies during app startup.
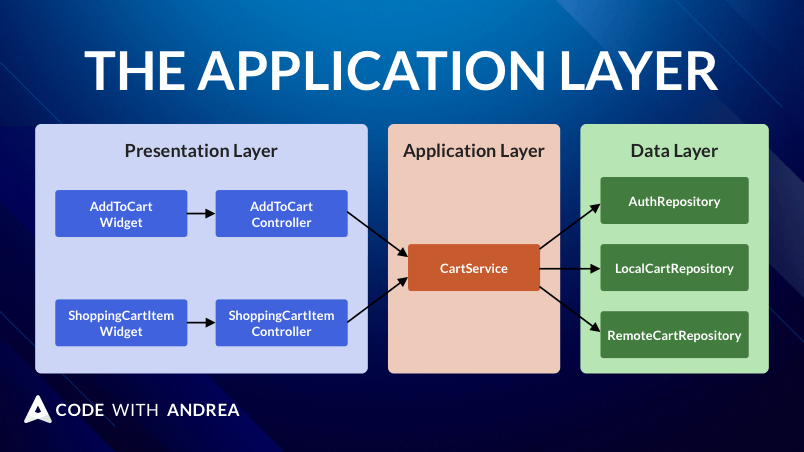
Service classes are the ideal place to store logic that depends on multiple data sources or repositories. Let's explore them by building a shopping cart feature.

The AsyncValue class from the Riverpod package offers a much nicer API compared to AsyncSnapshot from the FutureBuilder and StreamBuilder widgets. Here's how to use it.

When performing asynchronous work, we need to account for loading and error states in our UI. This article presents simple and reusable approach to handle this across multiple screens.

How to implement a responsive layout in Flutter by using a split view on large screens and drawer navigation on mobile.

How to create a reusable widget class that helps us when working with asynchronous data from Riverpod providers.

A detailed overview of a production-ready architecture that I've fine-tuned over the last two years. You can use the included starter project as the foundation for your Flutter & Firebase apps.